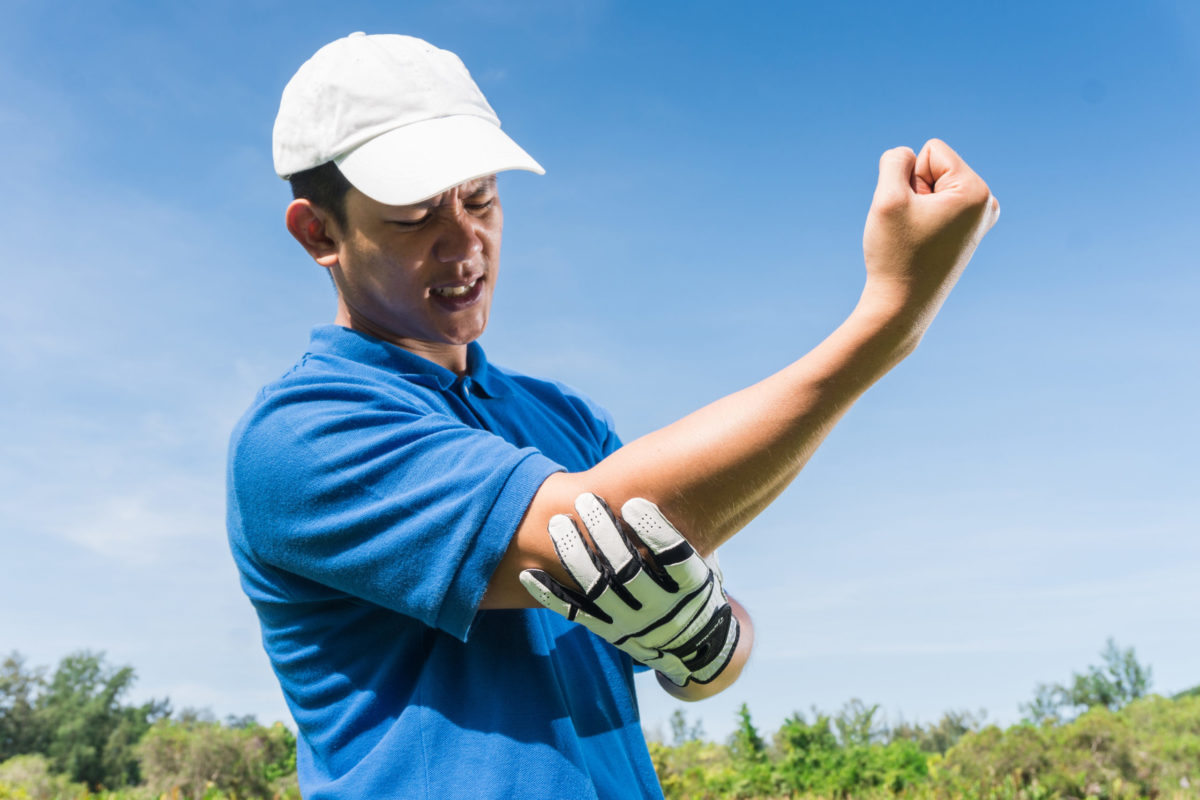
The elbow is one of the most complicated joints in your body. It’s crucial to performing day-to-day tasks, and any problems such as medial epicondylitis can drastically impact your quality of life.
As one of the most frequently exercised and stressed joints, the elbow is prone to injury. Examples include hyperextension and fractures, as well as orthopedic conditions like osteoarthritis and bursitis. While intermittent elbow and arm pain is usually not serious, it can cause considerable pain.
Without knowing what signs to look for, you could be suffering from elbow pain that is indicative of a more serious condition like medial epicondylitis. We’ll discuss what this condition is, how to identify it, and how to treat it.
What Is Golfer’s Elbow or Medial Epicondylitis?
Medial epicondylitis–more commonly known as golfer’s elbow–is a condition similar to tennis elbow, where inflammation and pain is present in the tendons of the forearm that connect the muscles on the inside of the elbow. It is also commonly caused by overuse but, in rare cases, can occur with no known repetitive motions. When you frequently use your wrist and arm to bend, grasp or twist things, your tendons can develop tiny tears that can cause wrist, elbow, and forearm pain.

Signs of golfer’s elbow are often felt when you bend and/or straighten your elbow, resulting in the following symptoms:
- Elbow to wrist pain
- Numbness
- Tingling
- Stiffness
Some sports activities that may increase the risk of developing epicondylitis include:
- Golf
- Baseball and other throwing sports, such as football and javelin
- Racquet sports, such as tennis
- Weight training
It’s not just sports that can cause medial epicondylitis. Repetitive manual work can also cause injury. Some occupations where golfer’s elbow is most prominently seen include:
- Painters
- Plumbers
- Construction workers
- Cooks
- Assembly-line workers
- Computer users
- Butchers
If pain in your elbow doesn’t improve, see an orthopedic specialist. They may ask questions about your daily activities, including your work duties, hobbies, and recreational activities.
How Is Epicondylitis Diagnosed?
Golfer’s elbow should be evaluated and diagnosed by an orthopedic specialist for proper diagnosis and treatment. Your specialist will perform the following:
- Medical history
- Physical examination
- An X-ray to rule out a fracture or arthritis as the cause of your pain.
- Occasionally, further tests such as an MRI scan or ultrasonography will be ordered to confirm the diagnosis of Medial Epicondylitis.
Medial Epicondylitis: At-Home Treatments
- Resting your arm. Halting activities that involve repetitive movements is one way to lessen symptoms, and gradually ease back into activities to avoid re-injuring yourself.
- A cold compress to reduce swelling, pain, and inflammation. Wrap ice in a towel and apply the compress to your elbow for up to 20 minutes, 3 or 4 times a day.
- Over-the-counter (OTC) medications. Ibuprofen and acetaminophen can reduce swelling and inflammation when taken as directed. For more severe cases, your doctors may recommend a steroid injection.
- Perform certain stretching exercises. Ask your doctor about safe exercises for stretching and strengthening your tendons. If you have weakness or numbness, you may be a suitable candidate for physical or hand therapy.
- Wearing a brace. Wearing a brace can reduce tendonitis and muscle strain.
More advanced and related treatments provided at EmergeOrtho, depending on your location, may include:
- Tennis Elbow Release
- Golfer’s Elbow Release
- Repair Biceps Tendon Ruptures at Elbow
- Cubital Tunnel Release (Ulnar Nerve at Elbow)
- Elbow Arthroscopy for Loose Bodies, Arthritis
- Releases for Stiff Elbows
- Ligament Reconstruction for Loose Elbows
- Operative Fixation of Elbow Fractures
- Operative Fixation of Forearm Fractures
Emerge Stronger. Healthier. Better. At EmergeOrtho–Triangle Region
Hopefully, you now have a more complete understanding of what medial epicondylitis is and what treatment options are available if symptoms worsen. We understand that elbow and arm pain can take you out of the activities you once enjoyed, which is why EmergeOrtho is committed to developing specifically tailored treatment plans to help you get back to your active lifestyle.
Self-schedule an appointment with an EmergeOrtho–Triangle Region specialist today to discuss your options. You can also call us any time at (919) 220-5255.